Table Of Contents
- Preparation
- Compartment
- Developing Serverless Application with Oracle Functions
- OCI Events
- Service Communication Patterns
- Deployments
- Container Engine for Kubernetes
- Object Storage
- API Gateway
- Resource Manager
- Key Management
- Streaming Service
Preparation
-
OCI Developer Learning Path - https://learn.oracle.com/ols/learning-path/become-oci-developer-associate/35644/75248
-
OCI Practice Labs - https://oracle.github.io/learning-library/oci-library/
-
OCI Practice Tests - https://learn.oracle.com/ols/module/practice-exam-for-oci-developer-2020-associate-certification/35644/75770
Compartment
-
Most resources can be moved between compartments
-
Atleast one policy required for accessing compartment
-
Compartments can be up to 6 levels deep
-
Sub compartments inherit permissions from the hierarchy
Developing Serverless Application with Oracle Functions
-
Max compute time 120 seconds
-
Max memory 1024 MB
-
It is built on enterprise-grade Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and powered by the Fn Project open source engine.
-
You can invoke a function that you’ve deployed to Oracle Functions in different ways:
-
Using the Fn Project CLI.
-
Using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure CLI.
-
Using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure SDKs.
-
Making a signed HTTP request to the function’s invoke endpoint. Every function has an invoke endpoint.
-
-
With Oracle Functions, you can write code in Java, Python, Node, Go, and Ruby
-
If you encounter an unexpected error when using an Fn Project CLI command, you can find out more about the problem by starting the command with the string
DEBUG=1and running the command again. -
You have to specify a policy statement to give the Oracle Functions service access to the network resources in the compartment:
Allow service FaaS to use virtual-network-family in compartment <compartment-name>
OCI Events
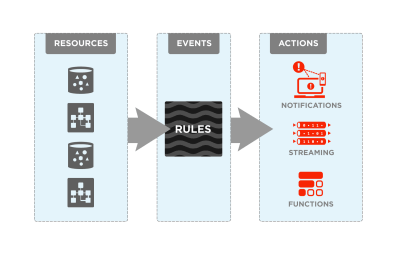
Service Communication Patterns
-
Service Aggregator Design pattern can be implemented as an aggregator service that invokes multiple services, collates the results, optionally applies business logic, and returns a consolidated response to the client
-
Circuit breaker pattern prevents the service from performing an operation that is likely to fail. For example, a client service can use a circuit breaker to prevent further remote calls over the network when a downstream service is not functioning properly
-
Service choreography is a global description of the participating services, which is defined by exchange of messages, rules of interaction and agreements between two or more endpoints. Choreography employs a decentralized approach for service composition. the decision logic is distributed, with no centralized point.
Deployments
-
Blue-green deployment is a technique that reduces downtime and risk by running two identical production environments called Blue and Green. At any time, only one of the environments is live, with the live environment serving all production traffic. For this example, Blue is currently live and Green is idle.
-
Canary deployments are a pattern for rolling out releases to a subset of users or servers. The idea is to first deploy the change to a small subset of servers, test it, and then roll the change out to the rest of the servers.
Container Engine for Kubernetes
-
OCI Service Broker for Kubernetes is an implementation of the Open Service Broker API. OCI Service Broker for Kubernetes is specifically for interacting with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services from Kubernetes clusters.
-
OCI File Services and OCI Block Volume can be used as persistent volumes.
-
Persistent volume claims must request a minimum of 50 gigabytes
-
kubectl explaincommand is used to list the fields for supported resources -
If you provided a public SSH key when creating the node pool in a cluster, the public key is installed on all worker nodes in the cluster. On UNIX and UNIX-like platforms (including Solaris and Linux), you can then connect through SSH to the worker nodes using the ssh utility (an SSH client) to perform administrative tasks.
-
To create an internal load balancer hosted on a public subnet, add the following annotation in the metadata section of the manifest file:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-internal: "true" -
To create an internal load balancer hosted on a private subnet, add both following annotations in the metadata section of the manifest file:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-internal: "true"andservice.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-subnet1: "ocid1.subnet.oc1..aaaaaa....vdfw" -
By default, load balancers are created with a shape of 100Mbps.
Object Storage
-
storage tier → standard/archive
-
Can encrypt using oracle managed (or) customer managed keys
API Gateway
Having created an API gateway and deployed one or more APIs on it, you’ll typically want to limit the rate at which front-end clients can make requests to back-end services. For example, to:
-
maintain high availability and fair use of resources by protecting back ends from being overwhelmed by too many requests
-
prevent denial-of-service attacks
-
constrain costs of resource consumption
-
restrict usage of APIs by your customers’ users in order to monetize APIs
"type": "STOCK_RESPONSE_BACKEND" indicates that the API gateway itself will act as the back end and return the stock response you define
You can use request policies to:
-
limit the number of requests sent to back-end services
-
enable CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) support
-
provide authentication and authorization
Resource Manager
-
CONFIGURATION - Information to codify your infrastructure. A Terraform configuration can be either a solution or a file that you write and upload.
-
JOB - Instructions to perform the actions defined in your configuration. Only one job at a time can run on a given stack
-
Plan - Parses your Terraform configuration and creates an execution plan for the associated stack. The execution plan lists the sequence of specific actions planned to provision your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources.
-
Apply - Applies the execution plan to the associated stack to create (or modify) your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources.
-
Destroy - Releases resources associated with a stack. Released resources are not deleted.
-
Import State - Sets the provided Terraform state file as the current state of the stack. Use this job to migrate local Terraform environments to Resource Manager.
-
STACK - The collection of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources corresponding to a given Terraform configuration. Each stack resides in the compartment you specify, in a single region; however, resources on a given stack can be deployed across multiple regions.
Key Management
- Waiting period 7-30 days
Streaming Service
-
Retention → 7 days
-
Max msg size → 1 MB
-
Partition → 5 read/s and 1000 emit per/s , read rate 2 MB/s write rate 1 MB/s
-
CONSUMER - An entity that reads messages from one or more streams.
-
CONSUMER GROUP - A consumer group is a set of instances which coordinates messages from all of the partitions in a stream. Instances in a consumer group maintain group membership through interaction
-
A consumer can read messages from one or more streams. Each message within a stream is marked with an offset value, so a consumer can pick up where it left off if it is interrupted.