Building a Near Real-Time Human-Like Outbound Calling System with Amazon Bedrock Nova Models (Nova Pro/Nova Sonic), Connect & Lex
28 Sep 2025
Reading time ~7 minutes
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- How the Pieces Fit Together
- Step 1: Create a Connect Instance
- Step 2: Configure a Bedrock Agent
- Step 3: Lambda Setup for Agent Invocation
- Step 4: Create a Lex Bot
- Step 5: Integrate Lex with Connect
- Step 6: Test Outbound Call
- Summary
Introduction
Imagine a system that doesn’t just place calls but speaks in near real-time, with human-like voice, to verify details or collect information from a user/IVR.
By combining Amazon Connect for outbound calls, Amazon Lex for natural voice interaction, and Amazon Bedrock Agents for conversational logic, you can build a system that feels less like a bot and more like a real agent.
This guide walks you through creating a proof-of-concept outbound call system that calls, converses naturally, and follows strict conversational rules.
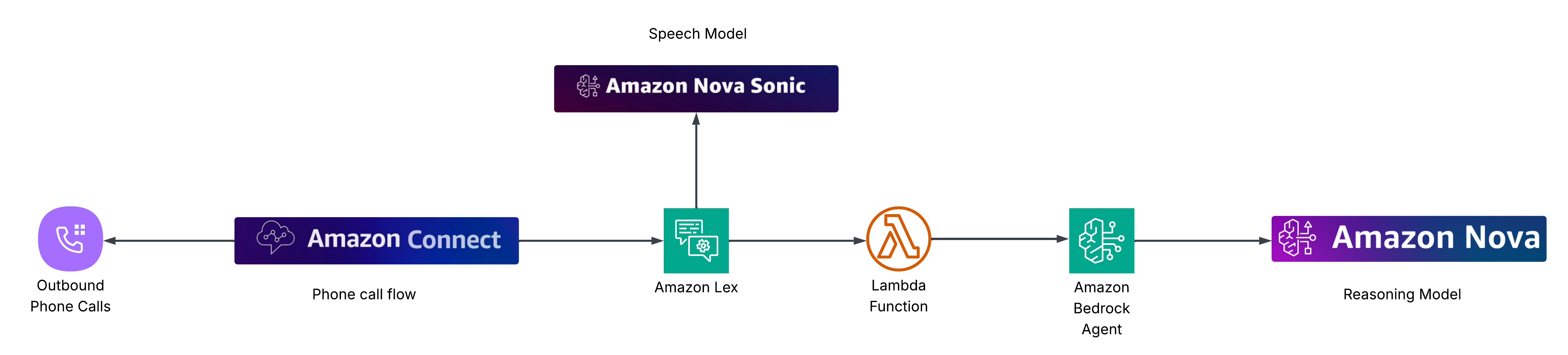
How the Pieces Fit Together
Let’s look at the big picture:
- Amazon Connect – Think of this as your call center platform. It makes the outbound call to the clinic.
- Amazon Lex – The conversational AI that handles voice interaction.
- AWS Lambda – A bridge that forwards what the user says to the Bedrock Agent.
- Amazon Bedrock Models/Agent – The brains of the operation.
- Nova Pro - Nova Pro is part of the Amazon Nova model family, offering a balanced mix of accuracy, speed, and cost efficiency. It supports a wide token limit (300k tokens) and is well-suited for a variety of generative AI tasks including conversational agents.
- Nova Sonic - Nova Sonic is a speech-to-speech foundation model available in Amazon Bedrock. It unifies speech recognition and speech generation into a single model, enabling near real-time, expressive voice conversations that adapt to tone, pacing, and conversational nuance. Nova Sonic supports user interruptions, multi-language use, and low latency streaming
So the flow looks like this: 👉 Connect (call) → Lex (conversation) → Lambda (bridge) → Bedrock Agent (logic)
Step 1: Create a Connect Instance
Amazon Connect is the starting point because it handles the outbound phone call.
- Go to the AWS Console and open Amazon Connect.
- Create a new instance. This will act as your virtual call center.
- Configure a contact flow for outbound calling. This is basically the script for how the call should proceed.
💡 At this point, you have the dialer ready, but it doesn’t yet know how to have a conversation.
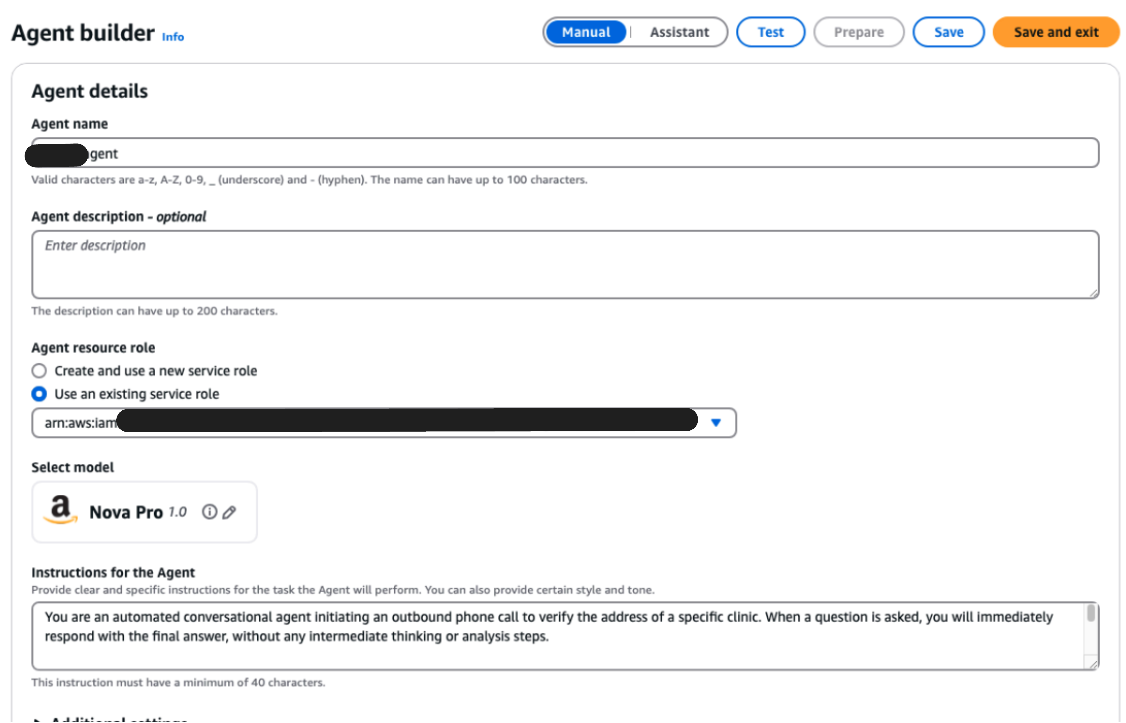
Step 2: Configure a Bedrock Agent
Now let’s give the system some intelligence by setting up an agent in Amazon Bedrock.
-
Open Bedrock → Agents in the AWS Console.
-
Use the Agent Builder to define how the conversation should work.
-
Here we chose Nova Pro as the model which will serve as our reasoning engine for the conversations.
-
Write down your agent instruction prompt here such as:
- Always introduce yourself as calling from XYZ.
- Never guess the company name or address.
- Ask politely for the address, confirm it, and end the call once complete.
-
Prepare the agent, then publish a version and alias so it can be invoked later.
💡 This step is where you lock in the strict rules, so the agent doesn’t go off-script.
Step 3: Lambda Setup for Agent Invocation
Amazon Lex can’t directly talk to a Bedrock Agent, so we need a Lambda function as a translator.
- Create a new AWS Lambda function.
- Attach the
AmazonBedrockFullAccesspolicy so it can call Bedrock. - Use the following sample code:
import os
import logging
import boto3
import json
from datetime import datetime
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
AGENT_ID = "xxxxxxxx"
AGENT_ALIAS_ID = "xxxxxxxx"
AWS_REGION = os.environ.get("REGION_NAME", "us-east-1")
bedrock_agent_runtime = boto3.client("bedrock-agent-runtime", region_name=AWS_REGION)
def json_serializer(obj):
"""JSON serializer for objects not serializable by default json code"""
if isinstance(obj, datetime):
return obj.isoformat()
raise TypeError(f"Object of type {type(obj)} is not JSON serializable")
def is_conversation_complete(agent_response):
"""Check if the conversation is complete based on agent response"""
logger.info(f"[CONVERSATION_CHECK] Checking if conversation is complete for response: '{agent_response[:100]}...'")
completion_indicators = [
"thank you for your assistance",
"conclude the call",
"goodbye",
"have a great day",
"that's all i needed",
"address recorded",
"information received",
"end the call",
"call is complete",
"conversation complete"
]
response_lower = agent_response.lower()
logger.info(f"[CONVERSATION_CHECK] Response (lowercase): '{response_lower[:100]}...'")
for indicator in completion_indicators:
if indicator in response_lower:
logger.info(f"[CONVERSATION_CHECK] ✅ COMPLETION DETECTED: Found indicator '{indicator}' in response")
return True
logger.info("[CONVERSATION_CHECK] ❌ CONVERSATION ONGOING: No completion indicators found")
return False
def lambda_handler(event, context):
logger.info(f"[LAMBDA_START] Starting lambda handler with event: {json.dumps(event, default=str)}")
user_input = event.get("inputTranscript", "")
session_id = event.get("sessionId", "")
logger.info(f"[INPUT] User input: '{user_input}'")
logger.info(f"[SESSION] Session ID: '{session_id}'")
# Get current session state if available
current_session_state = event.get("sessionState", {})
logger.info(f"[SESSION_STATE] Current session state: {json.dumps(current_session_state, default=str)}")
if not user_input:
logger.warning("[INPUT_EMPTY] No user input provided, returning error response")
return {
"sessionState": {
"dialogAction": {"type": "ElicitIntent"},
"intent": {"name": "FallbackIntent", "state": "InProgress"},
},
"messages": [{"contentType": "PlainText", "content": "Sorry, I didn't get your input."}]
}
final_answer = ""
try:
logger.info(f"[BEDROCK_CALL] Invoking Bedrock agent with input: '{user_input}'")
response = bedrock_agent_runtime.invoke_agent(
agentId=AGENT_ID,
agentAliasId=AGENT_ALIAS_ID,
sessionId=session_id,
endSession=False,
enableTrace=True,
inputText=user_input
)
logger.info("[BEDROCK_RESPONSE] Successfully received response from Bedrock agent")
event_stream = response['completion']
chunk_count = 0
for event in event_stream:
if 'chunk' in event:
chunk_count += 1
data = event['chunk']['bytes']
chunk_text = data.decode('utf-8')
final_answer += chunk_text
logger.info(f"[CHUNK_{chunk_count}] Received chunk: '{chunk_text[:50]}...'")
elif 'trace' in event:
logger.info("[TRACE] Received trace event")
logger.info("Trace: %s", json.dumps(event['trace'], indent=2, default=json_serializer))
else:
logger.warning(f"[UNKNOWN_EVENT] Unknown event type: {event}")
logger.info(f"[BEDROCK_COMPLETE] Final answer assembled from {chunk_count} chunks: '{final_answer[:100]}...'")
if not final_answer:
logger.warning("[BEDROCK_EMPTY] No response from agent")
final_answer = "No response from agent."
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"[BEDROCK_ERROR] Error invoking Bedrock agent: {str(e)}")
final_answer = "Sorry, there was an error processing your request."
# Determine if conversation is complete
logger.info("[FLOW_CHECK] Determining conversation completion status...")
conversation_complete = is_conversation_complete(final_answer)
if conversation_complete:
logger.info("[FLOW_DECISION] 🎯 CONVERSATION COMPLETE - Setting state to Fulfilled and closing")
return {
"sessionState": {
"dialogAction": {"type": "Close"},
"intent": {"name": "FallbackIntent", "state": "Fulfilled"},
"sessionAttributes": {"continueLoop": "0"} # Tell Connect to stop looping
},
"messages": [{"contentType": "PlainText", "content": final_answer}]
}
else:
logger.info("[FLOW_DECISION] 🔄 CONVERSATION ONGOING - Setting state to InProgress and eliciting intent")
return {
"sessionState": {
"dialogAction": {"type": "ElicitIntent"},
"intent": {"name": "FallbackIntent", "state": "InProgress"},
"sessionAttributes": {"continueLoop": "1"} # Tell Connect to keep looping
},
"messages": [{"contentType": "PlainText", "content": final_answer}]
}
💡 Think of Lambda as the middleman: it serves as a passthrough between Lex and Bedrock Agent. It also gives indications to Lex if the conversation continues or has ended.
Step 4: Create a Lex Bot
Now let’s build the Lex bot that powers the conversation.
- Open Amazon Lex and create a new bot.
- Provide the bot a name, create Lex permissions & enable error logs.
- In Add language, choose a generative AI voice option.
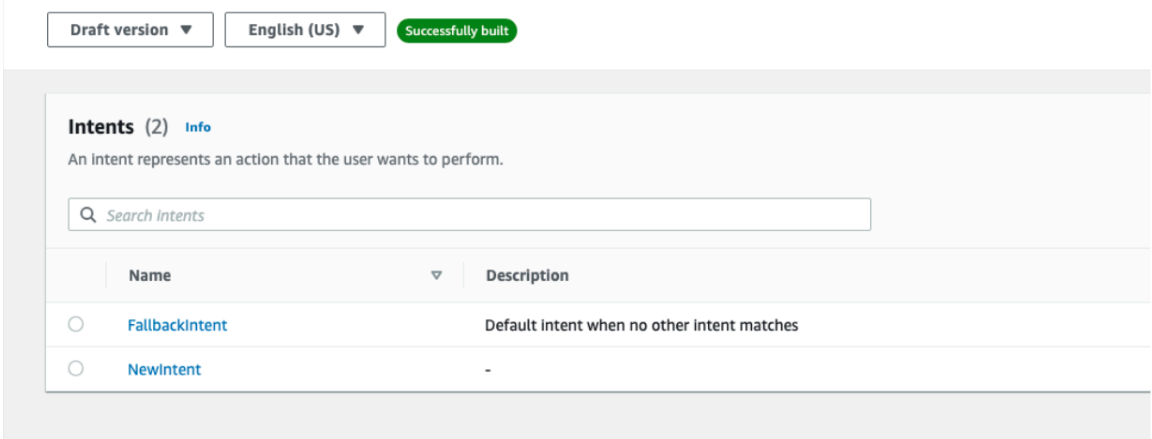
- In the default intent, enter “Do not use” keyword as a match so that it can be skipped and instead it will invoke our fallback intent.
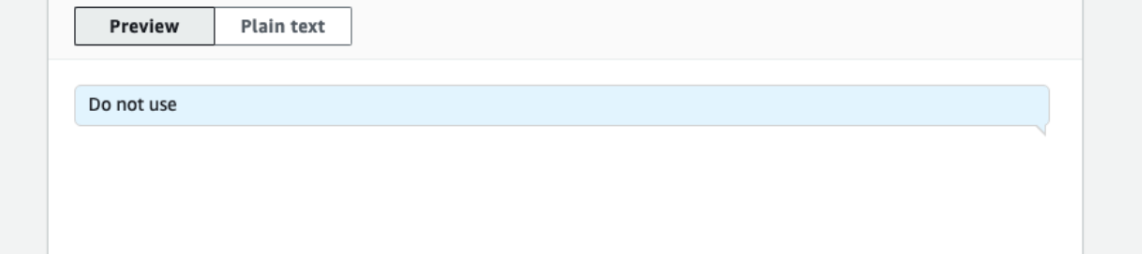
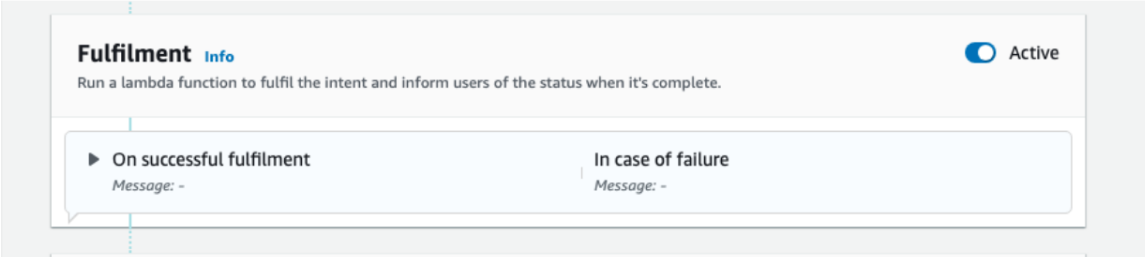
- Under FallbackIntent, go to Fulfilment section and enable it.
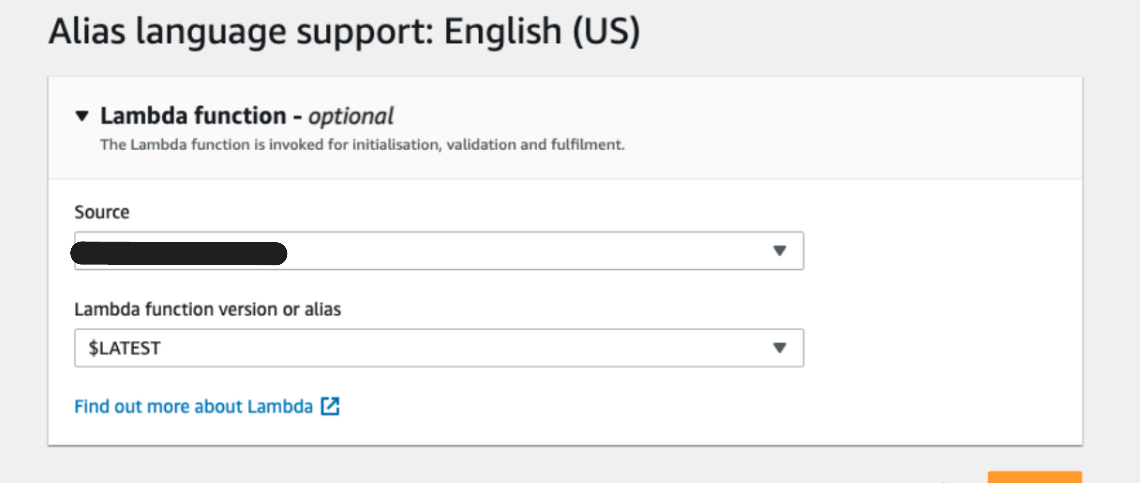
- Under Alias -> Languages -> English, Hook it up to your Lambda function from Step 3.
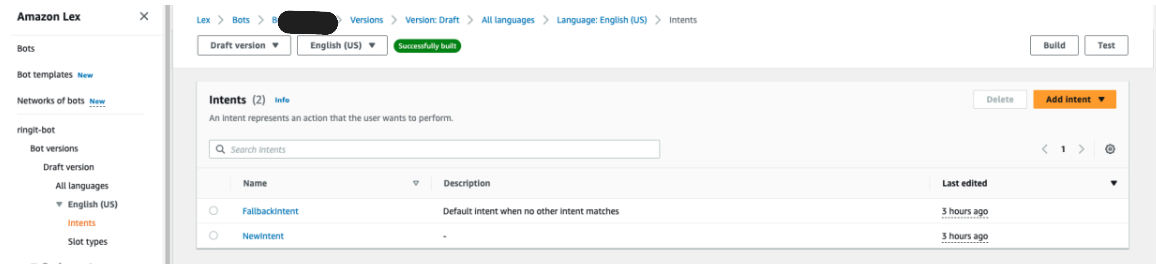
- Build and publish the bot.
💡 At this stage, Lex knows how to talk to people, but it’s relying on the Bedrock agent (via Lambda) for intelligence.
Step 5: Integrate Lex with Connect
Time to link the call system (Connect) with your conversational bot (Lex).
Go back to Amazon Connect.
Under Flows, add your Lex bot from previous step.
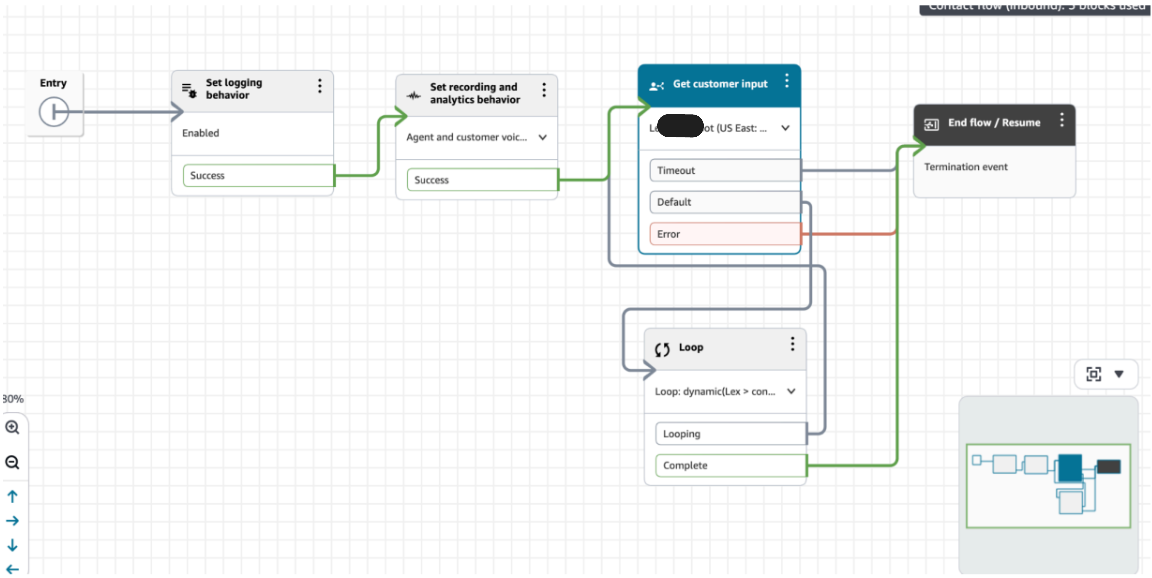
Below is a complete contact flow, with Lex bot as a step in the conversation.
Here we have set logging, enabled customer recording, integrated lex bot and looping to get continuous conversation flow.
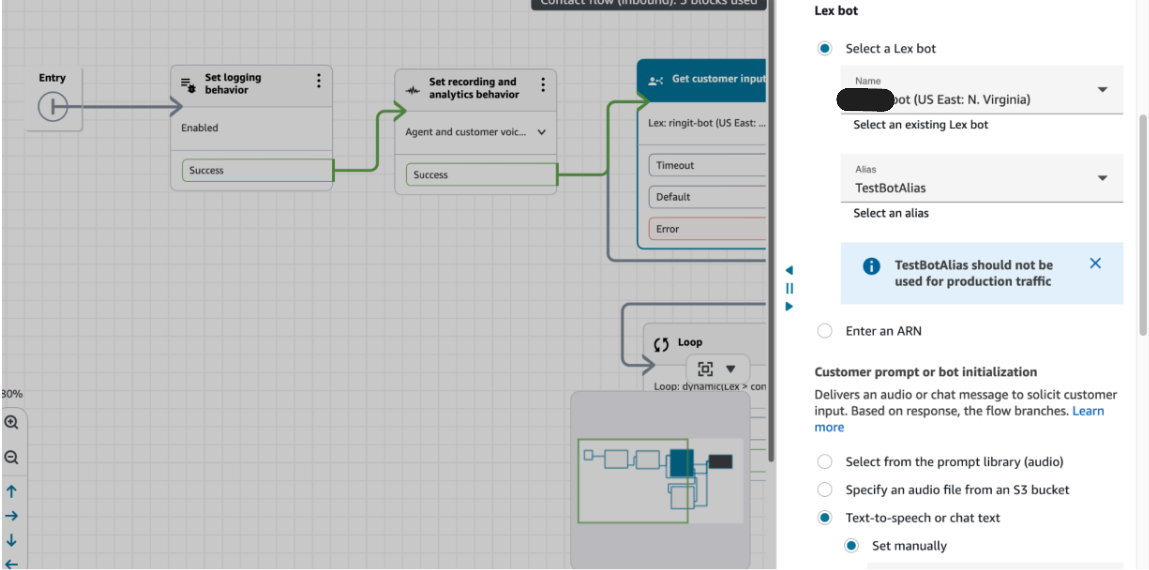
In the Lex bot, let’s do following configurations:
- Select the lex bot already integrated with connect.
- In the customer prompt, set Text-to-speech Set manually and give empty space in the box as we want the customer to initiate the conversation first.
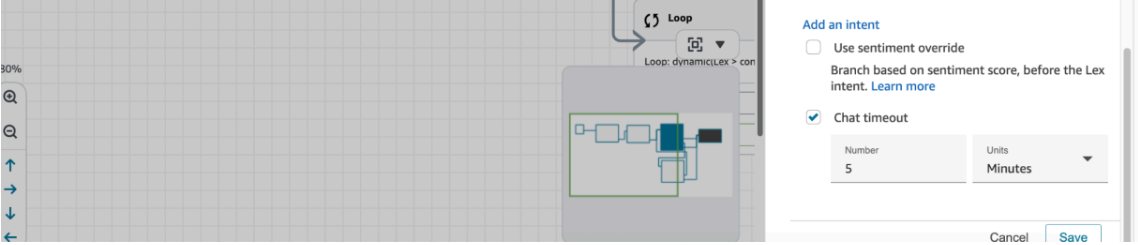
- Configure a suitable chat timeout.
- Add a session attribute which will drive our loop logic (note: we control this in the lambda function)
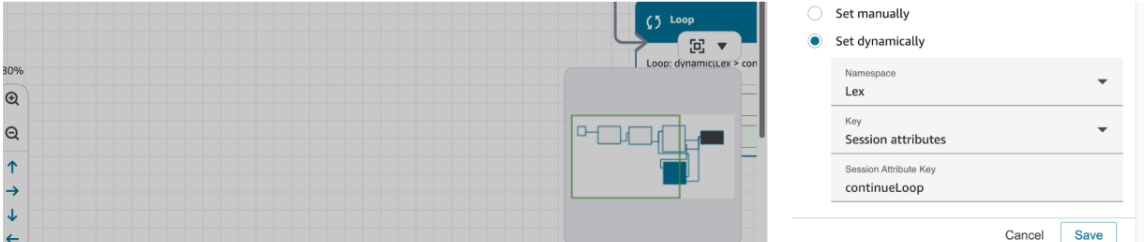
Save and publish the contact flow.
💡 Now, when Connect makes a call, it uses Lex to talk — and Lex secretly calls Bedrock via Lambda to figure out what to say.
Step 6: Test Outbound Call
Let’s give it a try. Use the AWS CLI to place an outbound call:
aws connect start-outbound-voice-contact \
--region us-east-1 \
--destination-phone-number "+15555555555" \
--contact-flow-id <CONTACT_FLOW_ID> \
--instance-id <CONNECT_INSTANCE_ID> \
--source-phone-number "+1834536456"
destination-phone-number→ Who you’re calling.source-phone-number→ Your Connect number.
💡 When the phone rings, Lex will handle the conversation, powered by the voice, rules and reasoning from Bedrock Nova models.
Summary
Here’s what we built:
- Amazon Connect → Makes the call.
- Amazon Lex → Handles conversation.
- AWS Lambda → Bridges Lex and Bedrock.
- Amazon Bedrock Agent → Provides strict conversational rules and interaction powered by LLM.
You can give the dynamic prompt in your lambda function to tailor your calls for outreach campaigns.
For post processing such as storing info back to DB or for verifications, you can make use of the recordings stored in S3 by Connect or generate transcripts in your lambda code which interprets the messages from Lex/Bedrock.
The result is a scalable outbound verification system that can run scripted, rule-based conversations automatically.